
A worker sorts cardboard at a recycling center in Newark, N.J. Photo: Jeff Greenberg/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
By Michaela Barnett, Founder, KnoxFill, University of Virginia, Leidy Klotz, Associate Professor of Engineering and Co-Director, Convergent Behavioral Science Initiative, University of Virginia, Patrick I. Hancock, Postdoctoral fellow, University of Virgini and Shahzeen Attari, Associate Professor of Public and Environmental Affairs, Indiana University via The Conversation • Reposted: July 25, 2023
You’ve just finished a cup of coffee at your favorite cafe. Now you’re facing a trash bin, a recycling bin and a compost bin. What’s the most planet-friendly thing to do with your cup?
Many of us would opt for the recycling bin – but that’s often the wrong choice. In order to hold liquids, most paper coffee cups are made with a thin plastic lining, which makes separating these materials and recycling them difficult.
In fact, the most sustainable option isn’t available at the trash bin. It happens earlier, before you’re handed a disposable cup in the first place.
In our research on waste behavior, sustainability, engineering design and decision making, we examine what U.S. residents understand about the efficacy of different waste management strategies and which of those strategies they prefer. In two nationwide surveys in the U.S. that we conducted in October 2019 and March 2022, we found that people overlook waste reduction and reuse in favor of recycling. We call this tendency recycling bias and reduction neglect.
Our results show that a decadeslong effort to educate the U.S. public about recycling has succeeded in some ways but failed in others. These efforts have made recycling an option that consumers see as important – but to the detriment of more sustainable options. And it has not made people more effective recyclers.
A global waste crisis
Experts and advocates widely agree that humans are generating waste worldwide at levels that are unmanageable and unsustainable. Microplastics are polluting the Earth’s most remote regions and amassing in the bodies of humans and animals.
Producing and disposing of goods is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions and a public health threat, especially for vulnerable communities that receive large quantities of waste. New research suggests that even when plastic does get recycled, it produces staggering amounts of microplastic pollution.
Given the scope and urgency of this problem, in June 2023 the United Nations convened talks with government representatives from around the globe to begin drafting a legally binding pactaimed at stemming harmful plastic waste. Meanwhile, many U.S. cities and states are banning single-use plastic products or restricting their use.
Upstream and downstream solutions
Experts have long recommended tackling the waste problem by prioritizing source reduction strategies that prevent the creation of waste in the first place, rather than seeking to manage and mitigate its impact later. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and other prominent environmental organizations like the U.N. Environment Programme use a framework called the waste management hierarchy that ranks strategies from most to least environmentally preferred.
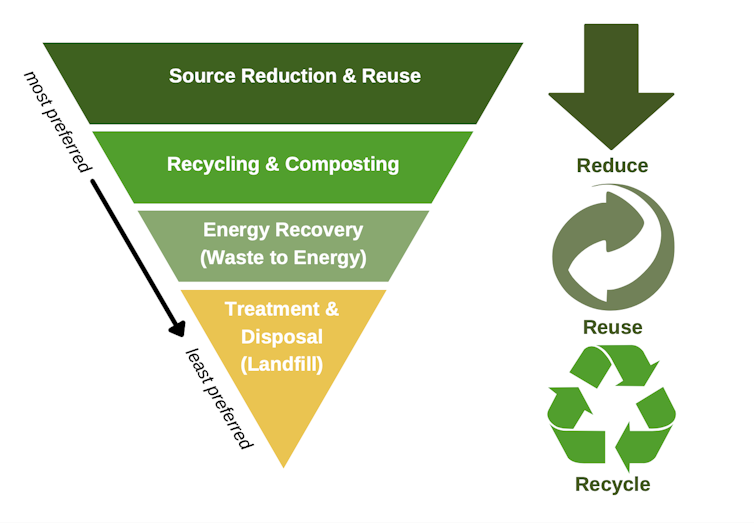
The familiar waste management hierarchy urges people to “Reduce, Reuse, Recycle,” in that order. Creating items that can be recycled is better from a sustainability perspective than burning them in an incinerator or burying them in a landfill, but it still consumes energy and resources. In contrast, reducing waste generation conserves natural resources and avoids other negative environmental impacts throughout a product’s life.
R’s out of place
In our surveys, participants completed a series of questions and tasks that elicited their views of different waste strategies. In response to open-ended questions about the most effective way to reduce landfill waste or solve environmental issues associated with waste, participants overwhelmingly cited recycling and other downstream strategies.
We also asked people to rank the four strategies of the Environmental Protection Agency’s waste management hierarchy from most to least environmentally preferred. In that order, they include source reduction and reuse; recycling and composting; energy recovery, such as burning trash to generate energy; and treatment and disposal, typically in a landfill. More than three out of four participants (78%) ordered the strategies incorrectly.
When they were asked to rank the reduce/reuse/recycle options in the same way, participants fared somewhat better, but nearly half (46%) still misordered the popular phrase.
Finally, we asked participants to choose between just two options – waste prevention and recycling. This time, over 80% of participants understood that preventing waste was much better than recycling.
Recycling badly
While our participants defaulted to recycling as a waste management strategy, they did not execute it very well.
This isn’t surprising, since the current U.S. recycling system puts the onus on consumers to separate recyclable materials and keep contaminants out of the bin. There is a lot of variation in what can be recycled from community to community, and this standard can change frequently as new products are introduced and markets for recycled materials shift.
Our second study asked participants to sort common consumer goods into virtual recycling, compost and trash bins and then say how confident they were in their choices. Many people placed common recycling contaminants, including plastic bags (58%), disposable coffee cups (46%) and light bulbs (26%), erroneously – and often confidently – in the virtual recycling bins.
This is known as wishcycling – placing nonrecyclable items in the recycling stream in the hope or belief that they will be recycled. Wishcycling creates additional costs and problems for recyclers, who have to sort the materials, and sometimes results in otherwise recyclable materials being landfilled or incinerated instead.
Although our participants were strongly biased toward recycling, they weren’t confident that it would work. Participants in our first survey were asked to estimate what fraction of plastic has been recycled since plastic production began. According to a widely cited estimate, the answer is just 9%. Our respondents thought that 25% of plastic had been recycled – more than expert estimates but still a low amount. And they correctly reasoned that a majority of it has ended up in landfills and the environment.
Empowering consumers to cut waste
Post-consumer waste is the result of a long supply chain with environmental impacts at every stage. However, U.S. policy and corporate discourse focuses on consumers as the main source of waste, as implied by the term “post-consumer waste.”
Other approaches put more responsibility on producers by requiring them to take back their products for disposal, cover recycling costs and design and produce goods that are easy to recycle effectively. These approaches are used in some sectors in the U.S., including lead-acid car batteries and consumer electronics, but they are largely voluntary or mandated at the state and local level.
When we asked participants in our second study where change could have the most impact and where they felt they could have the most impact as individuals, they correctly focused on upstream interventions. But they felt they could only affect the system through what they chose to purchase and how they subsequently disposed of it – in other words, acting as consumers, not as citizens.
As waste-related pollution accumulates worldwide, corporations continue to shame and blame consumers rather than reducing the amount of disposable products they create. In our view, recycling is not a get-out-of-jail-free card for overproducing and consuming goods, and it is time that the U.S. stopped treating it as such.
To see the original post, follow this link: https://theconversation.com/decades-of-public-messages-about-recycling-in-the-us-have-crowded-out-more-sustainable-ways-to-manage-waste-208924

















You must be logged in to post a comment.