
(Image credit: Markus Spiske/Unsplash)
By Mary Mazzoni from Triple Pundit • Reposted: April 10, 2024
Most financial professionals likely assume a strong return is all everyday investors are looking for as they save for their retirement. But even in a tough economy, a growing segment of global investors are equally concerned about aligning their money with their personal values, according to new research.
The global insights consultancy GlobeScan and the climate policy think tank InfluenceMap surveyed 5,000 retail investors — in other words, regular people who participate in 401(k) retirement plans and pension schemes or who dabble in purchasing individual stocks — to understand more about their preferences. Surveyed investors represent 10 countries and territories around the world, including the United States, Canada, Australia, France, Germany, Hong Kong and Japan.
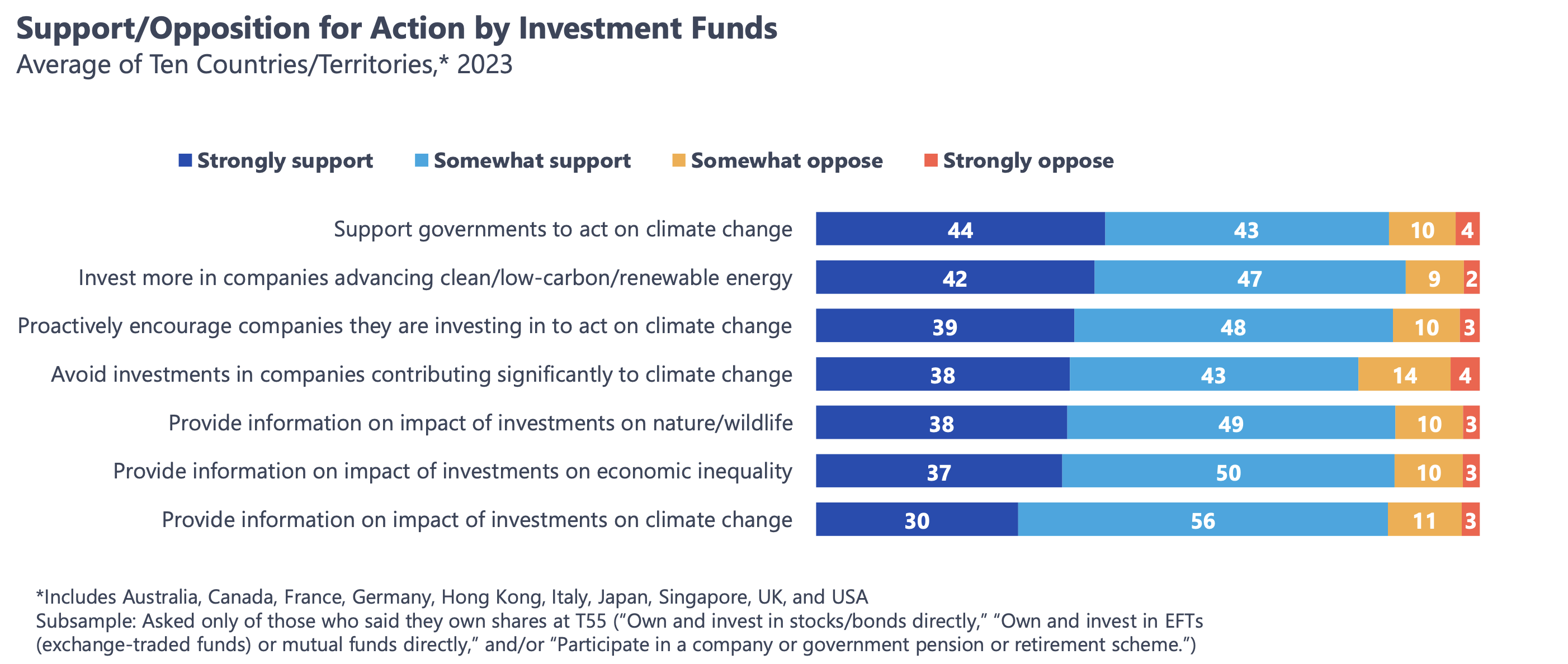
More than 8 in 10 of these investors (89 percent) either “strongly” or “somewhat” support investment funds putting money behind companies in the clean energy space, and 87 percent support funds actively encouraging the companies in their portfolios to act on climate change, according to the research. Further, over a third of surveyed investors strongly support funds excluding “companies that contribute significantly to climate change,” and another 43 percent somewhat support it.
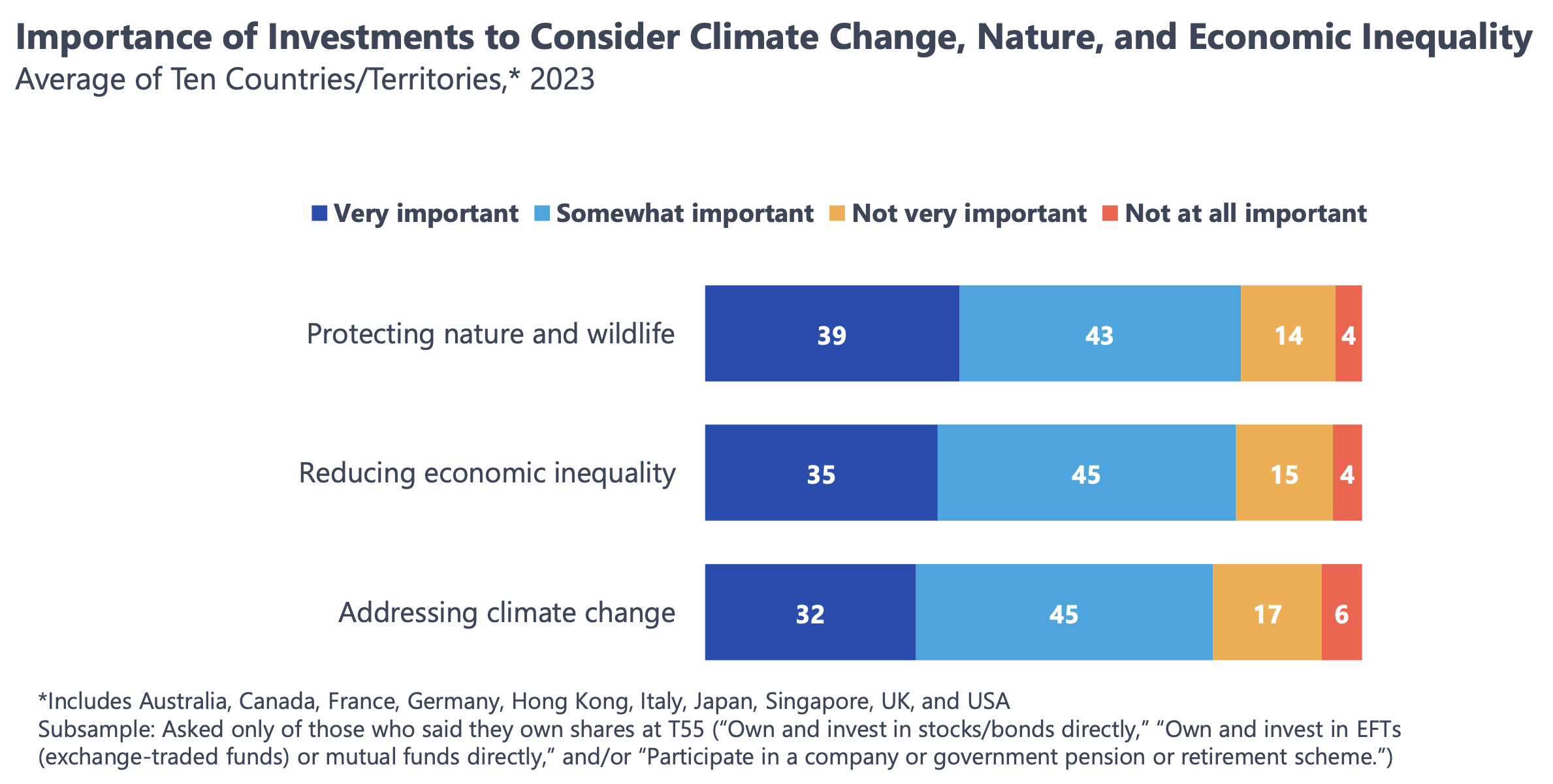
Many of these investors are also looking for the funds they do business with to provide information about how their investments impact nature and wildlife, economic inequality, and climate change, with more than 85 percent either strongly or somewhat supporting these disclosures.
“The financial system is all obviously predicated upon fiduciary responsibility and maximizing profits, but I don’t think the industry is very good at engaging their passive investors,” Chris Coulter, CEO of GlobeScan, told TriplePundit. “In this world of transparency and ability to reach people, we probably underestimate the innate, baseline sense of importance of sustainability issues for investment decisions among retail investors.”
How can funds align with investor preferences?
Findings like these dovetail with recent research from TriplePundit, in which more than half of surveyed U.S. consumers agreed it is “important” or “very important” for financial service companies to act responsibly when it comes to society and the environment. Over 30 percent said they switched their retirement fund provider in 2023 for sustainability reasons, according to the study conducted in partnership with 3BL, the research technology company Glow and panel partner Cint.
But even as sustainability becomes a more influential purchase driver for everyday investors, fund managers have been slow to respond.
“GlobeScan’s research shows the extent of retail investors’ demand for ambitious climate action by their fund and pension managers,” Daan Van Acker, program manager at InfluenceMap, said in a statement. “This stands in stark contrast to InfluenceMap’s findings that the world’s 45 largest asset managers are investing almost three times more assets in fossil fuel companies than green ones, while the proportion of managers with ambitious investee company stewardship has almost halved since 2021.”
Given the ongoing disconnect, research like this is a powerful tool for financial professionals interested in aligning their firms’ activities more closely with consumer preference.
“If I was in a fund and saw these metrics, I’d be intrigued, because you’re looking at 80 to 90 percent of people saying this stuff is important,” Coulter said. “There’s depth and foundational elements that even if you eroded a little bit, you still have significant majorities that are into this, so there’s an opportunity here.”
Still, growing political backlash against the use of environmental, social and governance (ESG) principles in investment decisions poses real risk for funds, particularly in the U.S. Among the recent examples, Texas’s Permanent School Fund pulled $8.5 billion out of BlackRock last week, arguing the asset manager’s focus on ESG hurts investors and runs counter to its fiduciary duties.
BlackRock stopped using the term ESG to describe its interactions with portfolio companies, citing increased weaponization of the term, CEO Larry Fink said last year. But the so-called “anti-ESG” backlash still cost the company an estimated $4 billion in assets in 2023.
Amidst this environment, fund managers would be wise to pay attention to the global interest in sustainability among investors, and perhaps test new offerings and policies in markets outside the U.S. first, Coulter advised.
“The context of the ESG politicization and the weaponization of these issues makes it much more challenging,” he said. “It’s only for the brave, probably, in the U.S. In most other markets, it’s much less of an issue. Testing in other markets outside the U.S., where there’s a bit of a stronger sense of interest and importance and also less risk around the anti-ESG backlash, would be a sensible thing to do.”
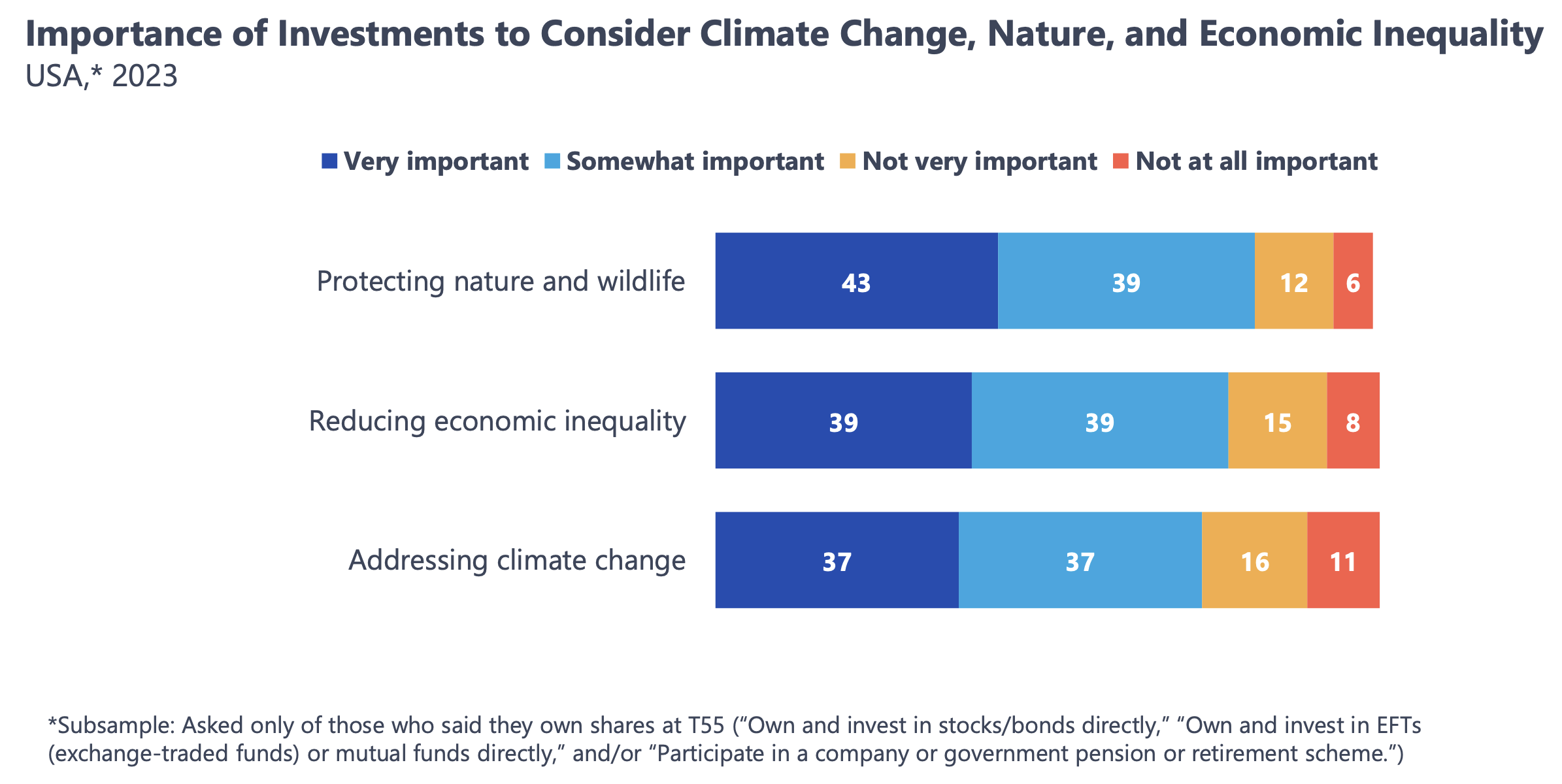
Taking note of these global trends — with an eye toward a continued strong interest in the U.S., where more than 70 percent of investors say it’s important for their investments to consider climate change, nature and economic inequality — can help fund managers maintain perspective in a difficult time.
“There’s a lot of noise out there, a lot of politicization, but the underpinning reality once this fever breaks is that there’s opportunity here to build something,” Coulter said. “Listening, understanding, getting close to people, hearing their own words, language and needs, and then finding ways to develop value propositions on the back of that, is really important.”
Messaging matters for funds, investors and the public
Even in the U.S., financial companies have an opportunity to connect with investors around issues that are less subject to political partisanship, with investments in nature, conservation and biodiversity being a clear example. Where the gravity of the climate crisis can easily overwhelm people to the point they tune out, the proactive, solutions-oriented tone of conversations around nature lend themselves to greater engagement among investors and the public, Coulter said.
“Winning on climate change means we avoid the apocalypse and we all don’t die. That is sort of the extreme expression of success on climate change and net zero, so it’s inherently negative or inherently focused on avoiding tragedy,” he explained. “Winning or being resilient on nature is infinitely positive in consumers’, retail investors’ and other stakeholders’ minds. You can always imagine a much more positive future for nature, and that means it’s got more energy and more possibility than just the climate conversation and decarbonization.”
Leaning into these areas with universal appeal can help fund managers to meet consumer preferences while providing much-needed funding to preserve natural resources, which also helps to fight climate change and promote economic equality.
Still, there is only so much that mainstream sustainable investing can do to drive progress. “With the trillions of dollars of assets under management that meet certain ESG criteria, it’s extraordinary numbers, and yet we don’t see any dramatic change in the impact that companies have on the environment or on people on the ground,” Coulter said. “There are two potential reasons for that. One is that it’s in the system now: There’s a lag in the system, while this amazing hockey stick impact curve is taking shape, and things will start to change dramatically because capital has been allocated in certain ways. Or two, the bar has not been high enough to differentiate what good looks like versus what average or status quo looks like.”
In particular, most sustainable funds apply negative screens to exclude entire sectors, such as oil and gas, or exclude companies with especially poor social and environmental records. But fewer have built funds around companies that have an especially positive impact on people and the environment, leaving investors with little information about how this approach would really perform. “Someone has to prove that the social impact approach actually delivers much more returns, and that’s still to be done,” Coulter said.
Research like this indicates the approach could be well received. “There’s an underlying value set that people have: People love nature, they’re worried about climate, and they care about inequality. And these are generally long-term investments, so it’s not about next quarter. It does change the future discounting risk for people that in the next 30 years, this makes sense. It’s very rational and it also fits with my values.”
Graphics courtesy of GlobeScan and InfluenceMap.
To see the original post, follow this link: https://www.triplepundit.com/story/2024/investors-interest-sustainability-esg/798556



You must be logged in to post a comment.