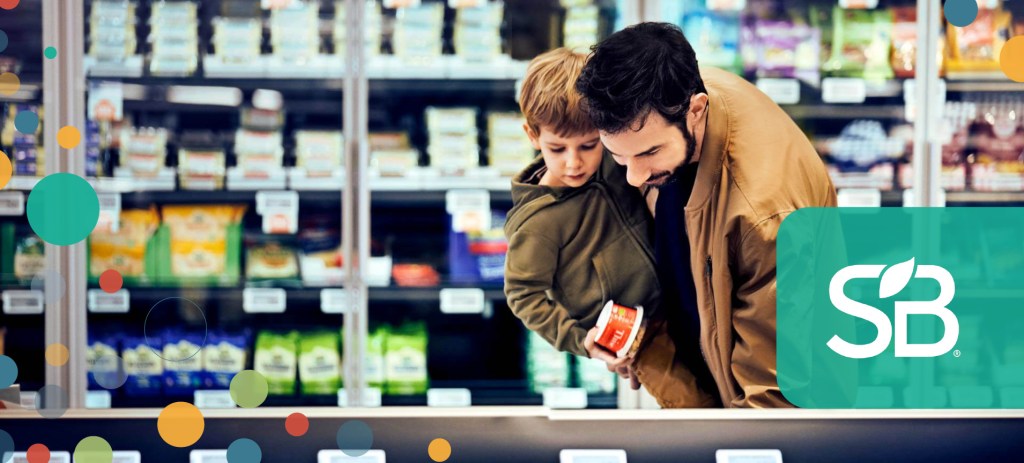

Image: Coop
Danish grocery giant Coop’s impactful partnership with Krukow Behavioral Design yielded insights for any retailer looking to enlist its customers’ help in reducing food-related carbon emissions.By Jeremy Osborn from Sustainablebrands.com • Reposted: June 16, 2023
Coop is a 1000+-store, member-owned grocery retailer founded and headquartered in Denmark. The popular national food chain has more than 2 million members (almost 1 in 2 Danes above the age of 18 are members!) and thousands of global suppliers, and provides in-store grocery experiences to more than 5 million customers every week. As such, it is uniquely positioned in Denmark to influence sustainable food-shopping behaviors as well as grocery supply chains worldwide.
The retailer is also hard at work addressing climate change — with an ambitious target of garnering 50 percent of its Scope 3 emissions reductions linked to the manufacturing of food via customer behavior change.
In May 2022, the company launched its “Climate Lab” — an initiative for testing innovative approaches to reducing emissions. The initiative was designed in phases, with the first phase being undertaken by Coop independently and the second in partnership with global behavioral science and nudge design experts Krukow Behavioral Design.
As Krukow founder and CEO Sille Krukow and Coop’s Head of Climate, Jonas Engberg, recently shared at SB Brand-Led Culture Change, the first phase of the initiative was a single-store experiment that, amongst other initiatives, involved a total rebranding of the store and introduction of a new core visual identity — as well as labeling 2,200 of the most climate-friendly products in the store to show customers the “most impactful” climate choice across a number of popular product categories. The idea was that presenting “choice-edited” options to customers would empower them to make more climate-friendly choices while shopping.
A brand guide to driving sustainable consumer behavior change
Download SB’s new, free guide to learn how your company can create an advantage in the marketplace through sustainable and innovative solutions that influence consumer behavior. The guide features case studies, a list of other helpful resources, and five actionable steps that brands and marketing teams can take to drive sustainable behavior change at scale.
While this initial experiment produced positive results, the Coop team learned that it needed a more holistic approach to behavior change — which led to the partnership with Krukow. This second phase — built on learning from the initial phase and expertise from Krukow — included store-wide interventions built on strengthening the single, visual vocabulary including vibrant, visual cues and many small, subtle nudges to guide customers towards more climate-friendly shopping choices and an overall climate-friendlier store visit.
“If you ask customers what they want, they will tell you they need better information in order to make better choices. But what they really need is for their environment to guide them towards these better choices holistically. Information is part of this, but it’s not enough on its own,” Krukow told Sustainable Brands®.
In phase two, the group created a “climate journey” through the store that guided and encouraged shoppers to purchase “more green and less red meat;” and with numerous small nudges towards climate-friendlier choices, Coop achieved a remarkable 14 percent reduction in the overall climate impact of shopping choices across all categories in a mere six months, as well as a 67 percent reduction in food waste. Remarkably, customer surveys showed a massive increase in awareness — from 7 percent to 65 percent of customers saying they felt they were being effectively guided to climate-friendly food choices.
Additionally, store data showed that the results did not skew to one demographic and that by creating a program that was, in Krukow’s words, “designed for the human brain” rather than for a specific demographic or target market, the interventions were effective in changing behavior across the board.
Coop found as well that its average shopper basket contains “less meat” on average than other stores.
A scalable success story
With a huge success in one store under their belt, Krukow and Engberg are now planning to scale their interventions to more stores. The phase-two program included 94 different, designed behavioral interventions; and the next step, according to Engberg, is to bring these to more stores.
“Scaling is not a huge cultural challenge for us, because 74 percent of customers have told us they wish to have more guidance towards climate-friendly shopping choices,” Engberg told SB. “And because we’ve shown in this initial pilot that encouraging climate-friendly food choices actually improves the bottom line, there is minimal resistance in the business.
“Staff at the store have been incredibly enthusiastic and have been essential co-creators and co-designers, as well,” he added. “They have the knowledge and the expertise of what works and doesn’t, and what customers want, in their individual stores. And we have a responsibility to make sure they can speak confidently to the initiative when customers ask questions like, for example, ‘why are bananas and avocados a climate-friendly choice? Don’t they have to travel very far?’”
Krukow agreed and emphasized the importance of holistic approaches:
“We’ve shown the power of using a holistic, in-store approach — leveraging employee expertise; and centered on the overall shopping experience that includes labeling, point-of-sale interventions, unified signage design and store layout. We’re excited to see Coop scale these successes across their operations.”
By designing these innovative behavior-led strategies, Coop has successfully engaged customers, improved its brand capital, reduced climate impact across all scopes, and increased profitability. The scalability of this initiative also provides a framework for other retailers to adopt — creating another opportunity to easily enlist consumers’ help to achieve company climate and sustainability goals.
To see the original post, follow this link: https://sustainablebrands.com/read/behavior-change/in-store-experiences-guide-shoppers-climate-friendlier-food
















































You must be logged in to post a comment.