
Photo: © Jennifer Adler
A trailblazing approach to marine conservation piloted in Seychelles finds new success in Belize.
By Julian Smith, Freelance Writer from the Nature Conservatory • Reposted: February 1, 2023
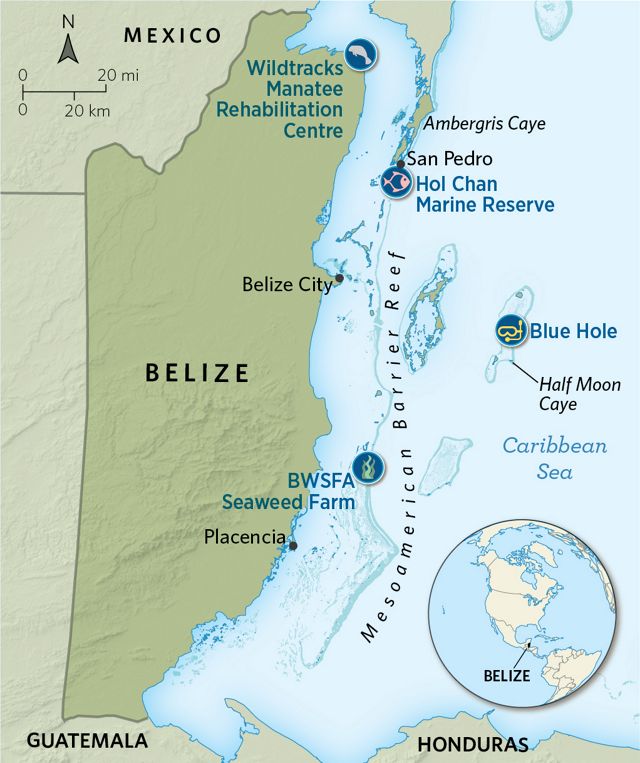
Scuba-diving the kaleidoscopic reefs of the Hol Chan Marine Reserve, just a 15-minute plane hop from Belize City, is like swimming into an Oscar-worthy underwater nature documentary. Sea turtles and spotted eagle rays soar past silently, while rainbow parrotfish munch algae off branches of healthy coral. A 3-foot nurse shark circles close by, while at the bottom of a small canyon—Hol Chan means “little channel” in Mayan—two male coral crabs face off like gladiators.
Hol Chan is the shining star of Belize’s myriad marine wonders and one of its busiest tourism destinations, but it’s just a small part of the longest barrier reef in the Western Hemisphere. Studded with hundreds of offshore atolls and cayes, Belize’s 240-mile coastline is home to more than 500 kinds of fish and three species of threatened sea turtle. Along the shore, mangrove forests, lagoons and estuaries shelter West Indian manatees and American crocodiles.
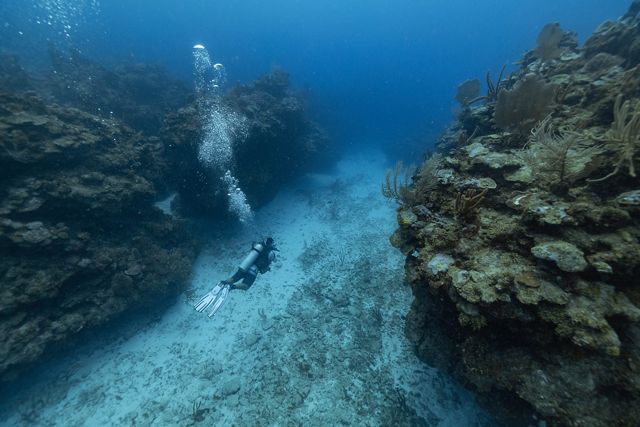

Although a portion of the barrier reef was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996, the entire reef is vulnerable to the effects of climate change, and most of it is also under increased pressure from overfishing and nearby development. By 2020, Belize’s public debt had reached $1.5 billion—larger than the country’s GDP—making it difficult to set aside money for environmental protection.
COVID-19 only made things worse. Visitation to Hol Chan has dropped drastically since 2019. Since entry fees cover most of the parks’ operations, the ranger staff is down from 15 to 11 (at one point last year there were only five). Before the pandemic, the park’s marine treasures were guarded around the clock; now, rangers are available only from 5 a.m. to 8 p.m.
Belize needed a solution that would preserve its natural capital and jump-start the industries that depend on it. The government looked to a financial transaction piloted by The Nature Conservancy in the Indian Ocean just a few years before. If that revolutionary model of marine conservation could find purchase on Belize’s Caribbean shores, it would restructure the country’s debt, freeing up tens of millions of dollars to protect its coastal and offshore resources—a transformative prospect for a country where nearly 50% of the population relies on the ocean for food and jobs.
The Nature Conservancy closed its first debt-for-ocean transaction in 2016 with the Republic of Seychelles, a far-flung island nation 1,000 miles off the east coast of Africa. The Conservancy created a financial mechanism, which would later become the underpinning of its Blue Bonds for Ocean Conservation program, to help Seychelles secure long-term funding for marine conservation. The Conservancy worked with the country and its creditors to help lower the financing rate for part of the nation’s debt, and helped find international grants to further support the transaction.
In exchange, the country committed to protect at least 30% of its marine territory and devotes part of its annual debt-payment savings toward conservation management.
It’s like a bank agreeing to refinance a home if the owner promises to put the savings toward improvements—just on a country-sized scale.
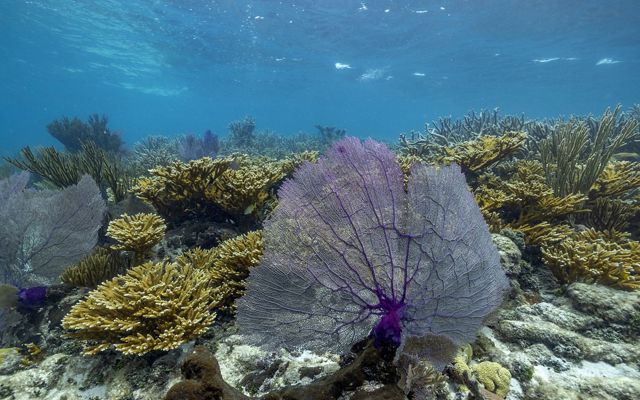

In the Seychelles, the program has been a resounding success. The $22 million debt restructuring has generated up to $430,000 per year for marine conservation and climate change adaptation. In less than five years, the country has been able to manage and protect more than 150,000 square miles of ocean, an area larger than Germany. The country has applied a wide scale of restrictions to these waters, including new marine preserves, dive-only sites, no-fishing zones and areas that are only open to community-level fishing.
Belize was a natural choice for the next Blue Bond, says Julie Robinson, program director for TNC in Belize, who spent much of her childhood in the town of San Pedro on Ambergris Caye, the gateway to Hol Chan. “As far back as I can remember, I was in the water exploring the seagrass beds, reefs and mangroves,” she says. “I was 6 years old when I decided I wanted to dedicate my life to protecting marine life.”
SEAWEED FARM
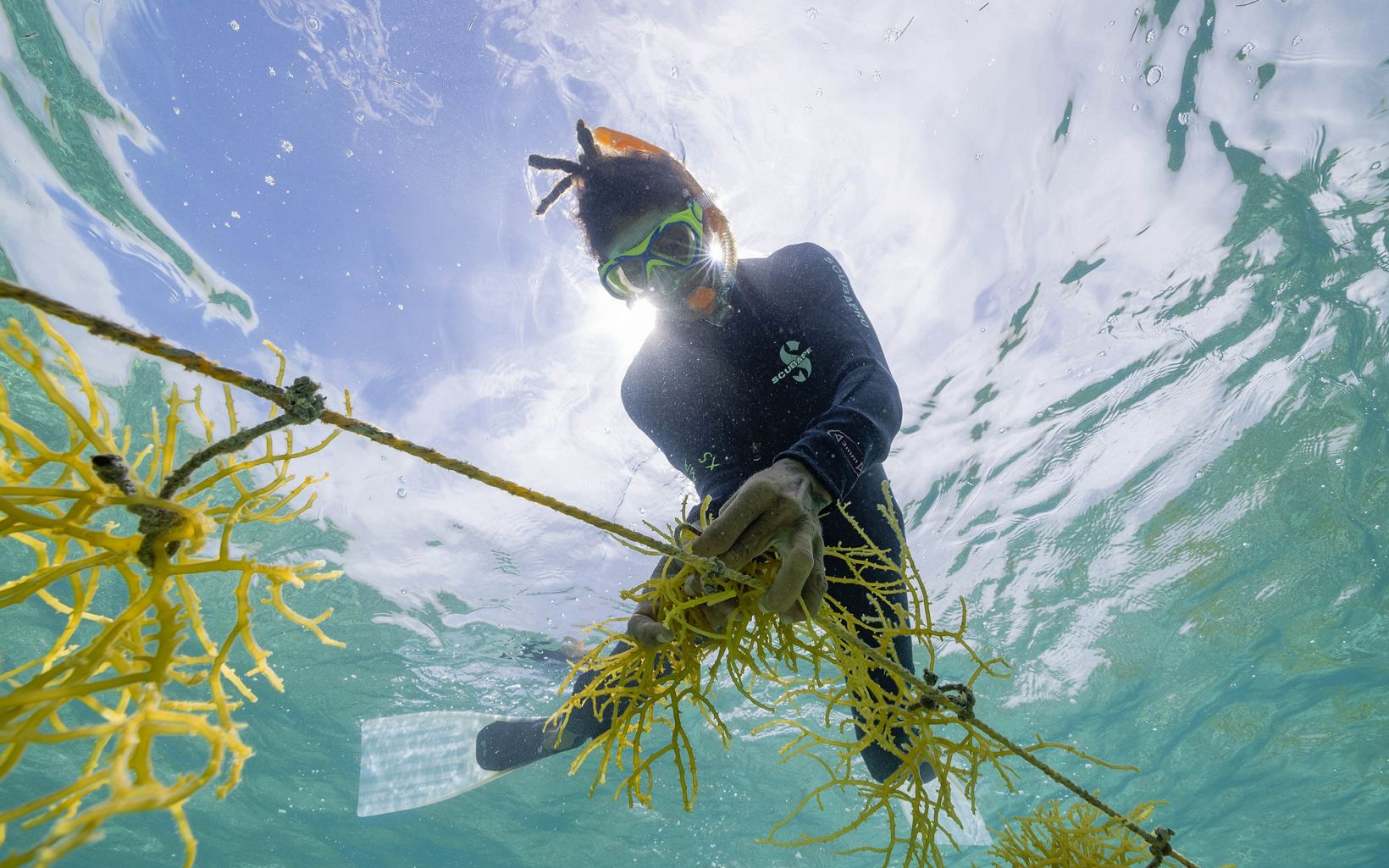
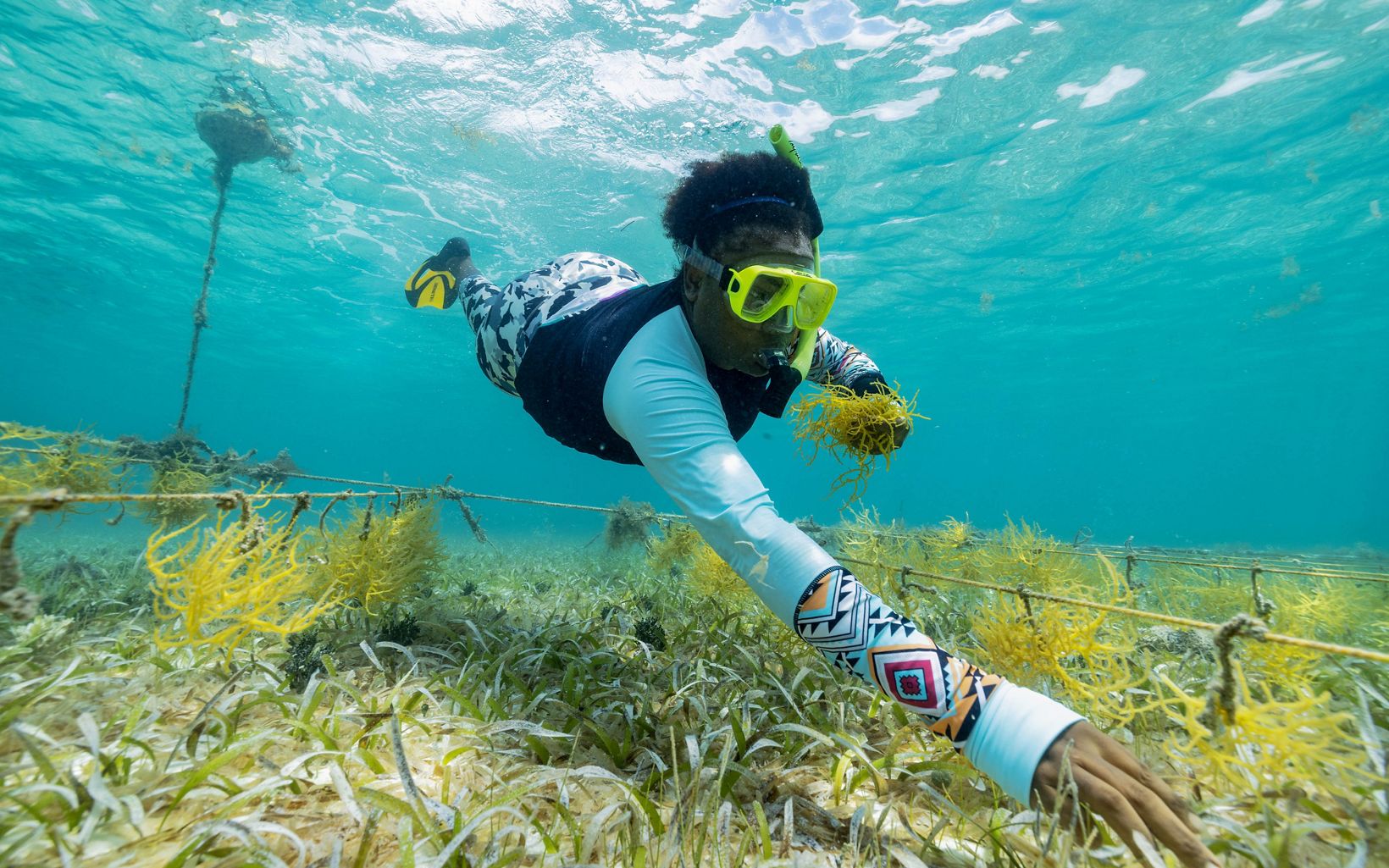
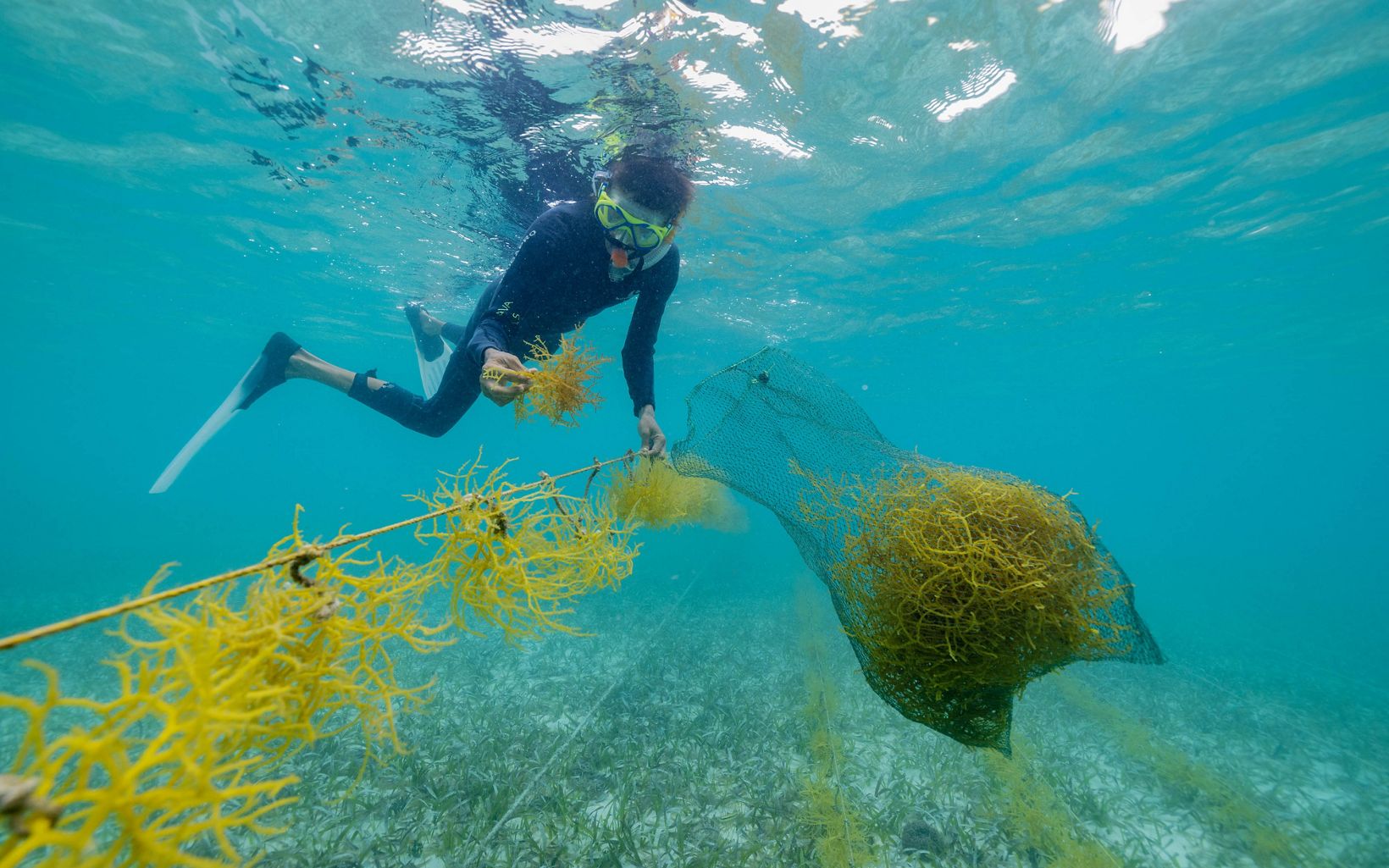






Such feelings are common among citizens of Belize. “We have a very strong connection to nature,” says Robinson. “We are proud of our country; everyone calls it ‘The Jewel.’”
Innovating strategies to conserve its dazzling terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity is nothing new for Belize. It was the first country in Central America to designate a Marine Protected Area, with the creation of Half Moon Caye Natural Monument in 1982. It was also the first to sign a subsidized “debt-for-nature” swap, an agreement finalized in 2001 that canceled $8.5 million in outstanding loans and protected 23,000 acres of its tropical rainforests.
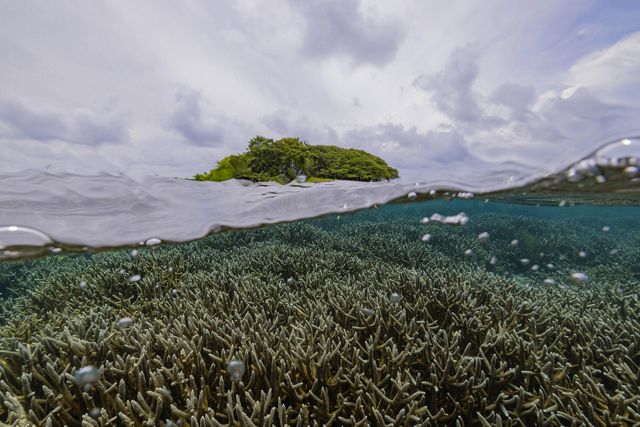

Taking Belize’s ocean conservation to scale was the next step, says Robinson. Nearly half of the country’s population lives in coastal communities, which rely on marine ecosystems for income, food and flood protection. Tourism accounts for 40% of the country’s economy, and a quarter of that is estimated to depend on coral reefs alone. Yet the annual budget to enforce environmental laws and expand protected areas has been less than $1 million.
To bolster the national economy and address that funding gap at the same time, the Belize government began initial discussions with TNC around a debt restructure for marine conservation in 2010. The road wasn’t easy, negotiations stalled, and the model was taken to the Seychelles instead, but a decade later, with Robinson at the helm, talks resumed in earnest. Finally, in November 2021, the Conservancy, along with global investment bank Credit Suisse and the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation, helped restructure $553 million of the country’s debt—ultimately reducing the principal by $250 million in the process. Over the next 20 years, as Belize pays down its new, more favorably termed loan, the savings are expected to generate $180 million to support in-country marine conservation. An endowment established through the transaction is designed to finance marine protection after the loan is repaid.
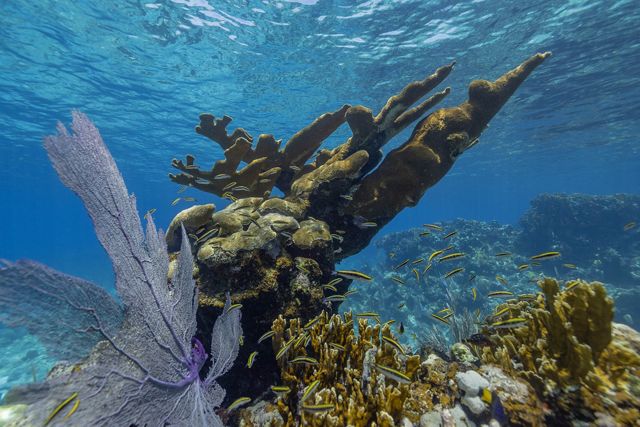

Along with the large-scale policy changes, the Blue Bond will also make more money available on the ground to support community ventures that promote Belize’s marine economy. One model for what these projects might look like floats just under the surface of the water, 18 miles offshore from the beach town of Placencia. Seven square wooden frames, 50 feet on a side, are attached by cables to the shallow sandy bottom. Long cords strung across the frames are lined with tangles of Eucheuma isiforme, a type of seaweed Belizeans use in cooking and as an ingredient in punches and smoothies. This sustainable seaweed farm is run by the Belize Women’s Seaweed Farmers Association (BWSFA), a nonprofit founded in 2019.
“We were looking for supplementary livelihoods because we can’t depend on fisheries or tourism anymore, because of climate change and depleted fish stocks,” BWSFA President Mariko Wallen says. “We decided to find a way to empower ourselves.”
The Conservancy helped the group set up a seaweed farming course and used satellite imagery to determine the best places for the farms, which also provide habitat for ecologically important and commercially valuable species like snapper, spiny lobsters and conch.
Wallen hopes the BWSFA can benefit directly from the Blue Bond by accessing funding to expand the farms, open a business arm for marketing and develop products like lotions, conditioners, soaps and cosmetics that could one day be sold abroad.
We are proud of our country; everyone calls it ‘The Jewel.’
Some citizens, like Wallen, will see the Blue Bond as a boon for their ocean-based livelihood, but 18 months of confidentiality around the deal—to avoid driving up the price of the Blue Bond before an agreement was struck—mean that there is some public relations work to be done to convince others. “We need to be able to show people how they directly benefit from it,” says Robinson. To address possible concerns that the deal will make more of the ocean off-limits to Belizeans, TNC is getting the word out by holding information sessions, producing educational videos and hiring new staff dedicated to engaging with stakeholders.
Community input is a large part of how the government will determine the types of protections that will be put into place. The goal is not to cut communities off from marine resources that they need for food or tourism, but to ensure enough areas are protected to make the entire system more sustainable.
The Blue Bond shows that it’s possible to balance economic development and conservation in a way that benefits everyone, Briceño says. “We have a responsibility to the planet and future generations to try to conserve as much as we can. That’s why this is so exciting: we can show that conservation is good business and that it can have a direct impact on the people most affected by climate change.”
To see the original post, follow this link: https://www.nature.org/en-us/magazine/magazine-articles/belize-blue-bonds/





















































You must be logged in to post a comment.